To install SVN server, run this command at the command prompt:
sudo apt-get install subversion apache2 libapache2-svn
Verify the installed version of Subversion software:
svn --version

We want to configure the apache in such a way that it’ll run on HTTPs and for this we need to enable ssl Apache2 module with a2enmod:
sudo a2enmod ssl
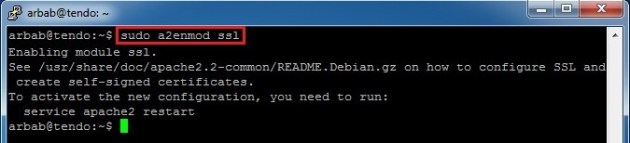
It will suggest you to restart apache;ignore that message for now.
Create a directory inside the /etc/apache2/ directory,where we’ll save the server key and certificate:
sudo mkdir /etc/apache2/ssl
Use this command for creating the self-signed SSL certificate and the server key that protects it, and save them into the new directory (/etc/apache2/ssl/):
sudo openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes -out /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.pem -keyout /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.key

Note: Fill the information accordingly!
Edit the ports.conf file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/ports.conf
Ensure that port 443 is defined as follows and add the NameVirtualHost for port 443:
NameVirtualHost *:443 Listen 443

Open up the SSL config file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl
Comment out the default certificate and key:
#SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem #SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key

And add the newly created certificate and key:
SSLCertificateFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.pem SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.key
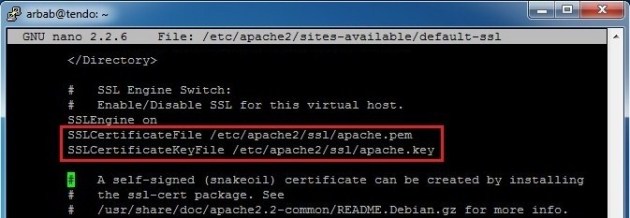
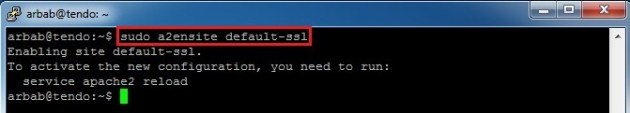
Now we need to configure the SSL site:
sudo a2ensite default-ssl
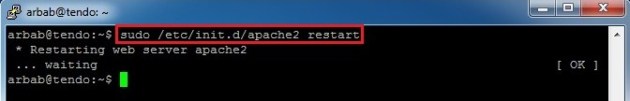
Restart the Apache service:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Now we should be able to connect to the server through SSL using Chrome or any other browser:

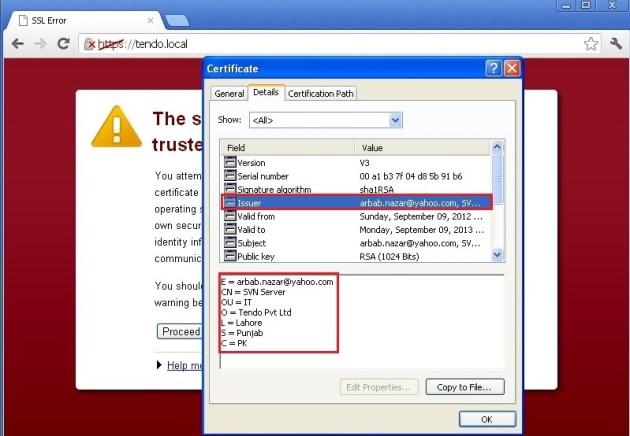
Verify the Certificate, that it’s the same that we created and configured:
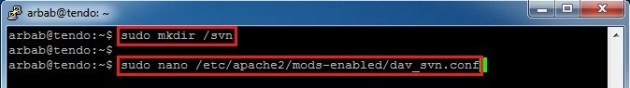
Next, we need to configure the SVN Server for this, make a directory where you want to keep the svn repositories and edit the dav_svn.conf file:
sudo mkdir /svn sudo nano /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dav_svn.conf
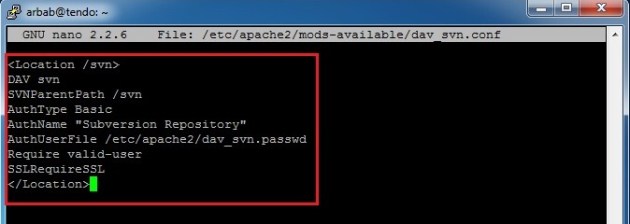
Delete all the data and make it simple like this:
<Location /svn> DAV svn SVNParentPath /svn AuthType Basic AuthName "Subversion Repository" AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd Require valid-user SSLRequireSSL </Location>
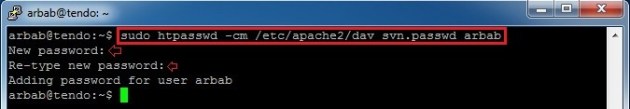
To create a svn user , use the following command:
sudo htpasswd -cm /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd arbab
We only need to use the -c option for the FIRST TIME, when you create a user, after that you will only use the -m option.
Move to the folder, where you want to keep your repositories and create your first repository:
cd /svn sudo svnadmin create myrepo

Make sure you set the permissions of the /svn directory to apache with the following command:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /svn
Restart the apache2 service:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart

Let’s test with the browser that our svn repository is accessible now through HTTPs at following url:
https://tendo.local/svn/myrepo
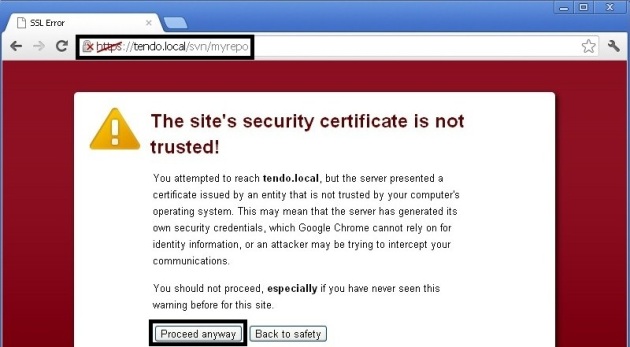
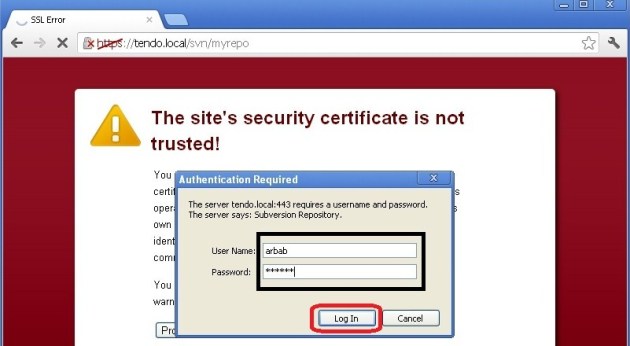
Click “Proceed anyway“, enter the username and password:
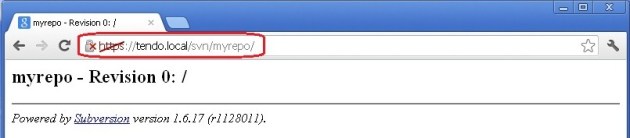
Yes, It is working
Note: Our SVN Server is also working with http:

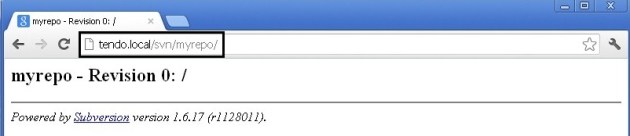
But, we don’t want that users access it through http, we only want to access it through https. To fix this, we need to edit the ports.conf file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/ports.conf
Comment these two lines:
#NameVirtualHost *:80 #Listen 80

Restart the apache2 service:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart

Now, try to access it through http, it’ll give us the rejection error:
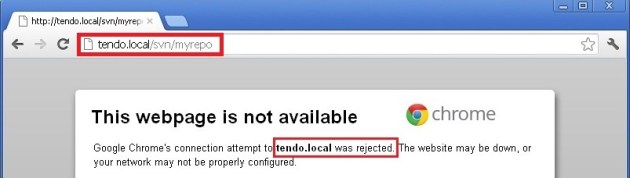
But with https, we can still access the svn repositories:

More Details Click Here
Author by:-rbgeek.wordpress
0 comments:
Post a Comment